Asset And Xontext (context) Transfers ( 1 )
Technical Specification: Xythum Protocol for Asset and Context Transfer
Version: 2.0
Authored by Xythum Labs
Abstract
Xythum Labs introduces a novel cross-chain interoperability protocol enabling asset transfers (token/value movement between chains) and context transfers (arbitrary data/state synchronization) through a decentralized, trustless architecture. By combining FROST threshold signatures, a distributed state ledger (SyncNet), and a programmable virtual machine (XythumVM) with a domain-specific language (XythumDSL), Xythum achieves sub- 1 5 -second finality for asset transfers and sub- 5 -second cross-chain event propagation. This document details the technical implementation of Xythum’s cross-chain infrastructure, focusing on its cryptographic primitives, network architecture, and developer tooling for building multichain applications.
** 1 . Introduction**
Blockchain ecosystems suffer from fragmentation, with $3T in total value locked (TVL) siloed across 1 5 0+ incompatible networks. Existing bridges operate as centralized custodians (e.g., 67% of cross-chain TVL relies on 9-node multisigs) or suffer from latency (3–30 minutes) and MEV vulnerabilities. Xythum redefines interoperability through:
- Asset Transfers: Non-custodial cross-chain swaps in 5 – 1 5 seconds via FROST signatures.
- Context Transfers: Generalized smart contract communication across chains via gateway contracts and XythumDSL.
- SyncNet: A verifiable UTXO-style ledger for transparent state management.
Fee market based on SyncNet state storage and MPCaaS compute units.
Definitions
2. 1 Asset Transfer
A mechanism to lock/mint or swap tokens between blockchains (e.g., BTC → ETH). Unlike traditional bridges, Xythum:
- Uses FROST threshold signatures (k-of-n nodes) for decentralized custody. Scales with nodes and operates on humongous infrastructure.
- Guarantees 1 : 1 asset backing via SyncNet-auditable reserves.
- Achieves 5 – 1 5 s finality through parallelized Schnorr signing rounds.
2.2 Context Transfer
A protocol for passing arbitrary data (events, state snapshots, function calls) between smart contracts on different chains. Enables:
- Cross-chain smart contract function calls (e.g., trigger Ethereum function from Solana).
- Historical state queries (e.g., fetch a contract’s balance 1 00 blocks ago).
- Conditional multichain logic (e.g., "If Bitcoin hits $ 1 00K, liquidate Solana position").
Technical Architecture
3. 1 Asset Transfer Implementation
3. 1 . 1 FROST Threshold Signatures
FROST (Flexible Round-Optimized Schnorr Threshold) enables decentralized signing with:
- Key Generation: Distributed Key Generation (DKG) across 1 ,000+ nodes.
- Signing Workflow:
1 . User locks assets on Chain A via Xythum’s Taproot-compatible deposit address (Bitcoin) or gateway contract (EVM).
2. SyncNet logs the lock event as an Intrinsic Transaction.
3. Nodes run FROST’s 2-round signing:
- **Round 1 **: Nonce generation + commitment broadcast.
- Round 2: Partial signature computation using secret shares.
- Coordinator aggregates signatures into a single 64-byte Schnorr sig. 5 . Relayer submits sig to Chain B’s gateway contract, minting wrapped assets.
Performance:
- Latency: 5 – 1 5 s (vs. 3+ minutes for MPC-based bridges).
- Security: 2 5 6-bit EdDSA curves, resistant to Wagner’s attack.
3. 1 .2 SyncNet Ledger
SyncNet provides verifiable proof of asset backing via:
- UTXO Model: Each transaction (lock, mint, burn) is recorded as:
SyncNet {
- Ledger (Main Chain)
- UTXO Database (Pending Orders)
- Transaction Processor
- State Synchronizer
- Consensus Engine
}
Transaction {
- Intrinsic (Incoming requests)
- Extrinsic (Outgoing/completion events)
- System (Network operations)
- Governance (Protocol updates)
- fee
- epoch begin etc
}
- Consensus: Nodes validate transactions via SPV proofs (Bitcoin) or Merkle-Patricia trie snapshots (EVM).
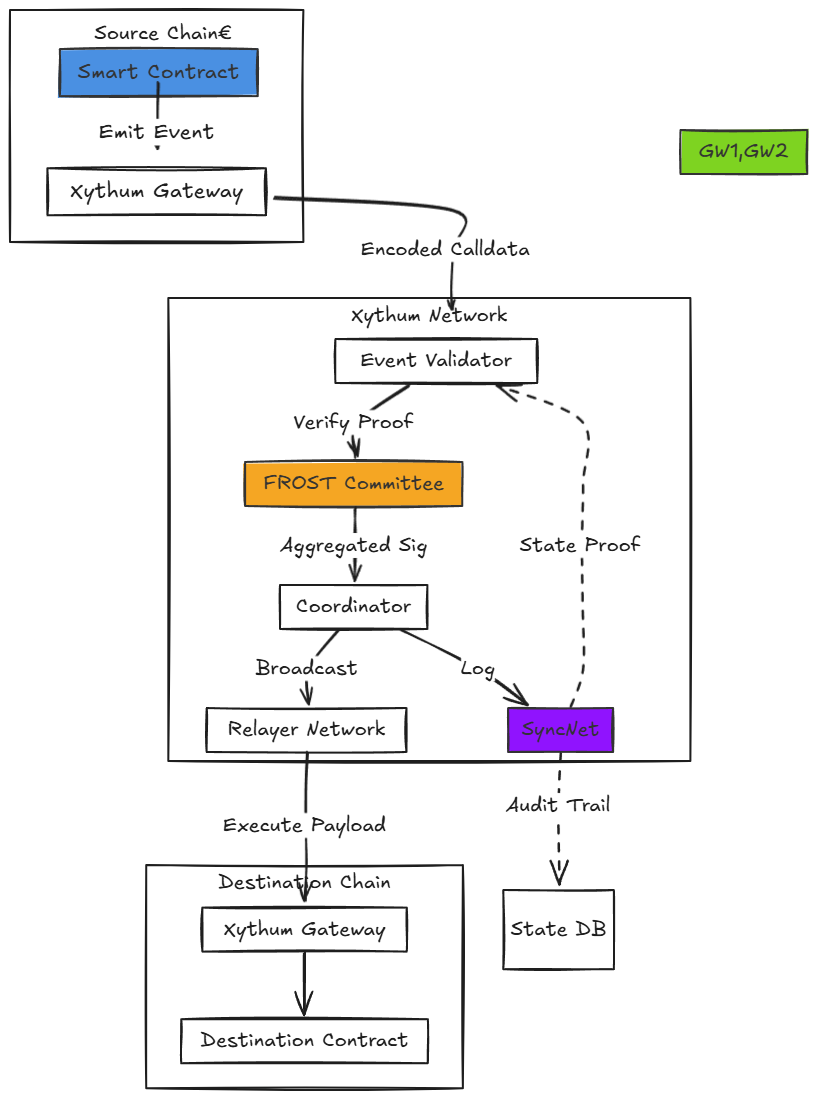
Context Transfer Implementation
3.2. 1 Gateway Contracts
Lightweight smart contracts deployed on all supported chains (EVM, Solana, Cosmos, Bitcoin via Tapscript):
contract XythumGateway {
event CrossChainMessage(bytes calldata, address destGateway);
function send(bytes calldata data, address destGateway) external {
emit CrossChainMessage(data, destGateway);
}
function execute(bytes calldata data, bytes calldata frostSig) external {
require(verifySig(frostSig), "Invalid signature");
(address target, bytes memory payload) = abi.decode(data, (address, bytes));
target.call(payload);
}
}
Workflow:
1 . Emit: Source contract calls XythumGateway.send(calldata, destChainGateway).
2. Consensus: Nodes aggregate the event into a FROST-signed message.
3. Propagate: Relayer submits signature + calldata to destination chain’s gateway.
4. Execute: Gateway decodes calldata and invokes target contract.
Latency: < 5 s for EVM-to-EVM, < 1 5 s for Bitcoin-involved transfers.
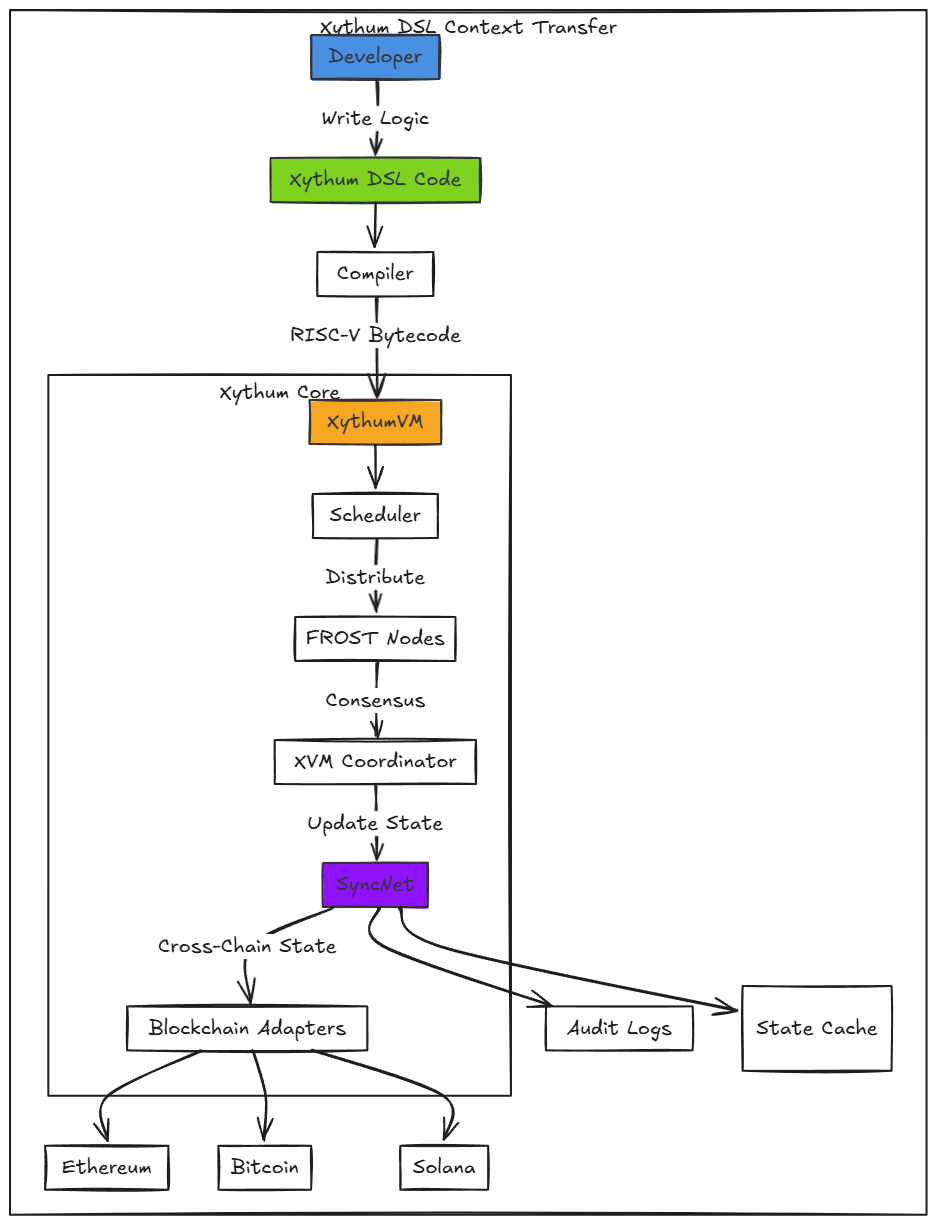
3.2.2 XythumVM & DSL
XythumVM: A deterministic VM supporting cross-chain state transitions:
- Chain Abstraction: Translates chain-specific opcodes (EVM, Solana, Bitcoin Script) into RISC-V instructions.
- State Proofs: Uses Merkle mountain ranges (MMR) for historical queries (e.g.,
get_state(chain, address, block)).
XythumDSL: A declarative language for multichain logic:
# Example: Cross-chain liquidation bot
def liquidate_on_btc_high():
btc_price = Chainlink(Arbitrum).get_price("BTC/USD")
sol_position = Solana(MangoMarkets).get_position(user_address)
if btc_price > 1 00000 and sol_position.collateral_ratio < 1 . 1 :
# Liquidate on Solana if BTC exceeds $ 1 00K
execute_on(
Solana,
"MangoMarkets.liquidate",
[user_address, sol_position.id]
)
Compilation:
1 . DSL → Intermediate Representation (IR). 2. IR → RISC-V bytecode with chain-specific adapters. 3. Deployed to XythumVM for cross-chain execution.
3.2.3 Bitcoin Compatibility
For non-smart contract chains (Bitcoin), Xythum uses:
- Taproot Addresses: Encode context transfer logic in Tapscripts.
- Time-Locked Transactions: CheckSequenceVerify (CSV) opcodes enforce XythumVM-resolved conditions.
4. Cryptographic Protocols
4. 1 FROST Optimization for Context Transfers
- Batch Signing: Aggregates multiple context transfers into one signature ( 1 ,024 txs/sec per shard).
- Sharding: BLS-based committee partitioning reduces node workload ( 5 0 nodes/shard).
Security Analysis:
- Schnorr vs ECDSA: Eliminates signature malleability, enables key aggregation.
- Adversarial Threshold: Resists up to (k- 1 )/n malicious nodes (k= 5 00, n= 1 ,000).
4.2 SyncNet Consensus
- Proof-of-Availability: Nodes stake $XYTHUM tokens to participate in SyncNet validation.
- Fraud Proofs: Slash misbehaving nodes via ZK validity proofs.
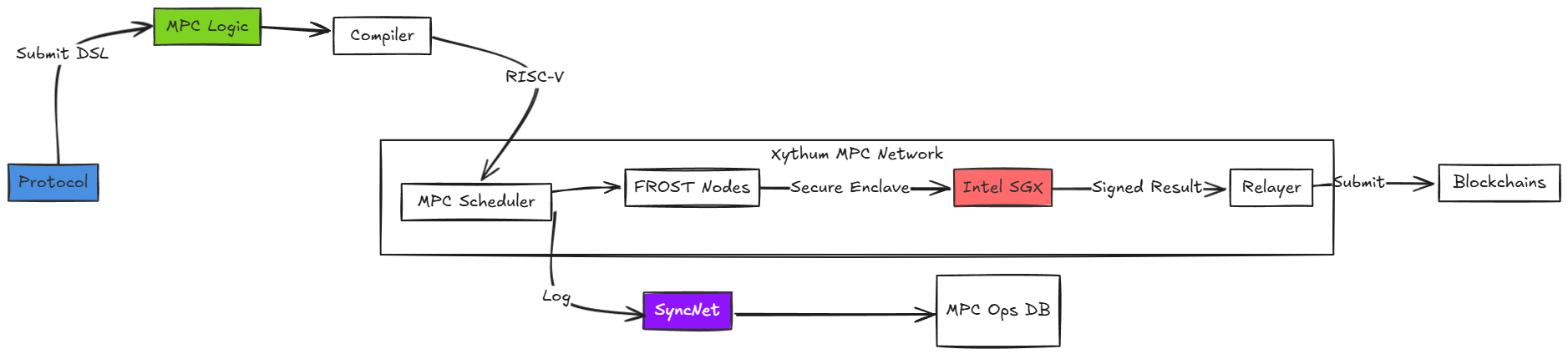
4.3 MPC-as-a-Service (MPCaaS) Architecture
- Infrastructure for bootstrapping decentralized networks.
- Garbled Circuits: Support for private function evaluation (e.g., dark pool order matching).
- Billing Model:
TODO
4.4 Use Case: Decentralized Exchange Bootstrapping
1 . Startup defines matching engine logic in Xythum DSL. 2. Xythum network provisions 5 00 nodes for order book management. 3. Revenue share: 1 5 % of exchange fees → Xythum treasury.
Components:
- Protocol Clients: Projects renting Xythum’s MPC slots (e.g., DeFi protocols).
- Slot Manager: Handles token-based slot allocation (gas fees per cycle).
- Garbled Circuit Executor: Supports custom MPC logic (e.g., threshold encryption).
- Relayers: Submit MPC results to target chains.
- Watcher Services: Monitor chain events for triggering MPC logic.
Flow:
1 . Protocol submits MPC logic (e.g., multisig wallet rules) in DSL. 2. Xythum compiles logic to RISC-V and charges gas fees. 3. MPC nodes execute logic, generating FROST-signed outputs. 4. Relayers submit results to destination chains (e.g., Solana). 5 . SyncNet logs MPC operations for transparency.
Use Cases
** 5 . 1 Cross-Chain Perpetual Futures**
- Position opened on Arbitrum, collateralized by Bitcoin.
- Liquidation triggered via XythumDSL when BTC price (from Chainlink) drops 1 0% on Ethereum.
** 5 .2 Multichain NFT Collections**
def update_nft_metadata():
eth_balance = Ethereum(Wallet).balance_of(user, "ETH")
sol_balance = Solana(Wallet).balance_of(user, "SOL")
total = eth_balance + sol_balance
if total > 1 000:
set_metadata(NFT, "tier", "platinum")
** 5 .3 Decentralized MPC-as-a-Service**
1 . Dev defines MPC logic in XythumDSL (e.g., t-of-n wallet recovery). 2. Xythum compiles it to RISC-V bytecode. 3. Protocol rents node capacity via $XYTHUM tokens (cost = cycles × gas price).
** 5 .4 Decentralized Bitcoin Lending**
1 . User locks BTC via Taproot time-locked address. 2. Xythum mints zkBTC on Ethereum with rate model:
interest_rate = 0.0 5 × utilization / ( 1 − utilization)
- Liquidation via FROST-signed Bitcoin transaction after 24h.
** 5 . 5 Chain-Agnostic Lending**
- Deposit BTC on Bitcoin as collateral.
- Borrow USDC on Polygon via SyncNet-verified proof of collateral.
- Repayment automatically unlocks BTC via FROST-signed release.
** 5 .6 Cross-Chain DAO Governance**
- Proposal created on Ethereum.
- Snapshot of token holders taken across 5 chains via XythumVM.
- Vote execution enforced on all chains via gateway contracts.
** 5 .7 Bitcoin-to-DeFi Swaps**
1 . Lock BTC in Taproot address (SPV proof logged on SyncNet). 2. Mint wrapped BTC on Avalanche via FROST-signed minting. 3. Swap to AVAX using Trader Joe’s liquidity pool.
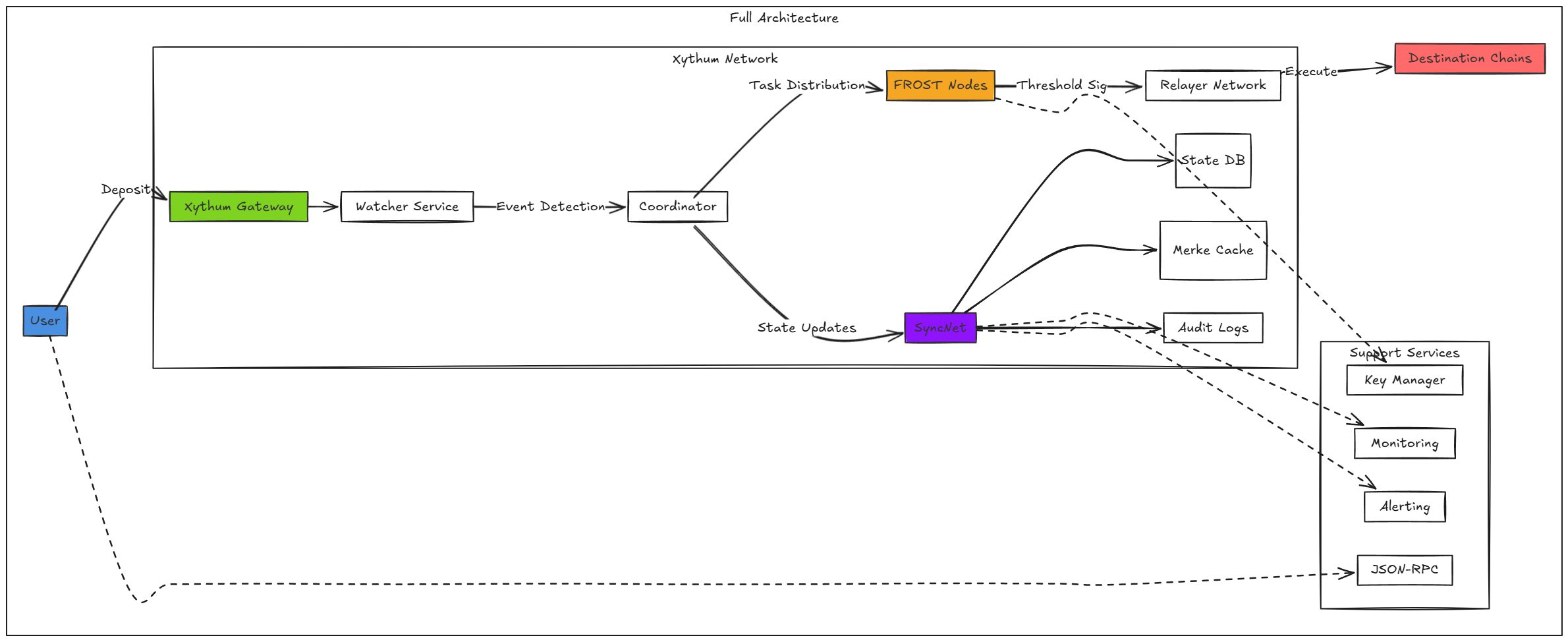
Diagrams Describing Context Transfers